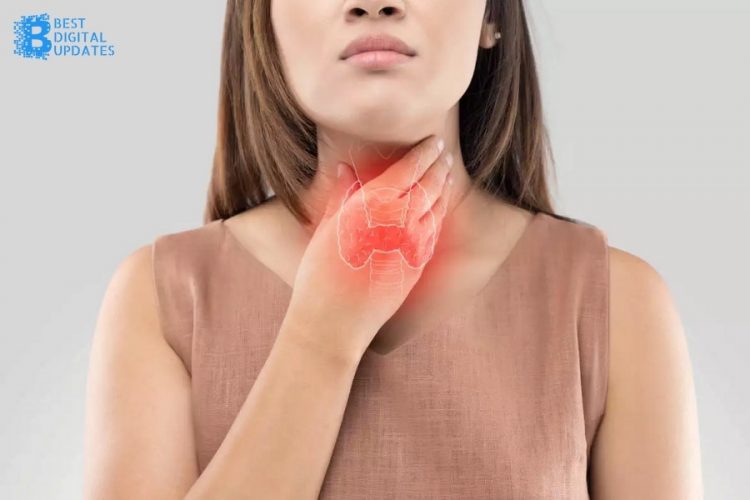
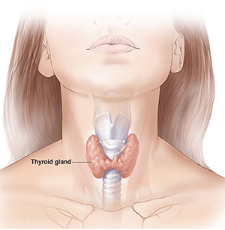
Postpartum hypothyroidism occurs when a female’s thyroid gland gets inflamed shortly after having her baby. This condition usually affects only a small proportion of pregnant women or around 3 in 1000 to 2 out of 100. The thyroid is a tiny gland at the back of the neck. Its primary function is to produce thyroid hormones, which regulate our metabolism and all our other hormones.
Most cases of this condition are not caused by a bacterial infection but because of the strong immune system response to the mother’s hormones. If you have developed postpartum thyroid’s, your body has either had an immature immune system, which leaves it unable to attack the invading bacteria, or that your immune system is not working efficiently, which impairs its ability to fight off the infection.
In both these cases, a standard treatment is antibiotics, which can be used to reduce inflammation. Antibiotics are generally given within a few hours of the onset of symptoms, so if you have developed postpartum thyroids, this would be the ideal time to commence treatment with antibiotics.
What Causes Postpartum Thyroiditis
Table of Contents
What causes postpartum thyroid disorder is still unclear to most people. This thyroid condition can be hazardous, and you must understand that it’s widespread but not very serious at all. Postpartum thyroiditis is usually an early warning sign of thyroid cancer.
Thyroid tumors can sometimes cause this thyroid condition and exposure to radioactive iodine, medications used to treat thyroid cancer, certain kinds of high cholesterol, and certain types of diabetes. The symptoms are mostly fatigue and weight loss, and they are most noticeable between two to four weeks after the woman gave birth to the child. A new mother must get proper sleep, and they can use essential oils to get adequate sleep, but they must handle essential oils with care. They can also use wedge pillows for getting optimum comfort. The Wedge pillows come in different sizes and you can choose one based on your need.
When a pregnant woman experiences postpartum thyroiditis, her body usually responds as if a virus has infected it. She may have a fever, chills, swollen lymph nodes, and muscle aches. You should also note that if you’ve had the postpartum hemorrhagic disease before, you might get re-infested by your body’s autoimmune thyroid disease response to any previous infection. In that case, you will need to take care of the infection before it worsens and kills you.
The best way to prevent this condition is to keep track of your hormone levels and your symptoms. You must be aware of how you feel every day. If you experience frequent colds or swollen glands, that is a solid indication of hyperthyroidism. Since beta-blockers only treat the symptoms and not the underlying problem, your symptoms will just come right back if you stop taking the medication.
You should also keep track of any medications you’re taking for your medication-free period because some manufacturers add a drug called progesterone to their products to counteract the effects of postpartum thyroiditis. This can worsen some people’s symptoms, so check with your doctor before using any medication while on the postpartum program.
Symptoms Of Postpartum Thyroiditis
Well, it is more common than you might think, and some of the symptoms include fatigue, constipation, and bloating. A lot of get sick with this problem… and a lot of the time it is very mild. But still, it isn’t enjoyable, and that’s why I’m going to tell you how to know if you have it. If you feel exhausted all the time or have trouble concentrating, you may have this problem.
There are many ways to diagnose a thyroid condition, but doctors have to do some blood tests and perform some scans to make an accurate diagnosis. Doctors may prescribe medications like prednisone, or they may recommend you use beta-blockers. Beta-blockers are drugs that stop your thyroid from making the necessary hormones for various problems, such as an overactive bladder, enlarged spleen, or a condition called hypothyroidism. To rule out other conditions such as diabetes or an underactive thyroid, these other conditions have to be ruled out first, and then the doctor can start treating your symptoms.
There are two types of thyroiditis, functional and structural. The experimental thyrotoxic phase occurs when your thyroid does not produce enough hormones. Its function is to produce the thyroid hormones for proper metabolism. The structural thyrotoxic phase happens when your thyroid gland produces too much hormone.
This usually leads to several symptoms such as severe weight gain, constipation, infertility, depression, rapid heart rate, joint pain, and fatigue. Sleep is an excellent remedy to deal with such issues. You can use different ways to treat such problems, like changing your mattresses, duvets, and duvet covers. A duvet cover is a fabric pouch that helps protect the duvet and is also comfortable on the outside. Also, you must reject the mattress that does not provide you enough comfort. You must also learn how to store a mattress.
The treatment usually depends on how severe your symptoms are. Medications are used during the hypothyroid phase to reverse the damage caused by hyperthyroidism. However, some patients also need hormone replacement therapy or surgery, depending on their medical histories.
Your doctor may treat your symptoms with medication, radiation, or surgery. You can avoid complications of postpartum thyroid disease if you are careful with your thyroid hormones after giving birth. Always keep a good diet plan, and exercise regularly. Be sure to check your body’s hormone levels regularly, particularly in the first few weeks after childbirth. A healthy lifestyle will not only improve your energy levels and well-being, but it will also protect your baby from specific health problems. Ensure that you take your prenatal vitamin every day after birth, and talk to your doctor about alternative treatments for symptoms.
Treatment
It is tough to diagnose the exact cause of postpartum thyrotoxicity, and often treatment is delayed until the cause has been established. A standard method of treatment is to treat the postpartum symptoms, avoiding potentially serious side effects. One of the most dangerous side effects of prolonged iodine deficiency (hypothyroidism) is that it can cause the thyroid to enlarge due to continued iodine deficiency, leading to chronic hyperthyroidism.
Treatment of the condition often consists of drug therapy (iodine and thyroxine, or TSH), but doctors sometimes recommend surgery if the cause of symptoms is suspected to be hyperthyroidism. Surgery for this condition usually involves removing one or more of the thyroid follicles (replaced with a balloon catheter), which causes the immediate removal of excess thyroid hormone production.
After a few weeks, normal thyroid function should begin to return. If thyroid hormone replacement therapy is required, doctors will usually give patients thyroid hormones at doses below the maximum daily recommendation; however, patients should be monitored regularly for signs of depression since severe depression can also harm thyroid hormone production.
Conclusion
The most common cause of postpartum thyrotoxicity is an underlying deficiency of vitamin D. This condition is treated with regular doses of vitamin D. Hypothyroidism patients should avoid a diet deficient in magnesium, as this can also result in underactive thyroid function. Severely underactive thyroid patients may require thyroxine supplements. Know best hair treatment for hair growth anf thickness.